LAENNEC

Laennec is the ethical drug manufactured with JBP’s unique technologies.
Laennec is the ethical drug manufactured with JBP’s unique technologies for effective extraction of variety of growth factors, cytokines, and other physiologically active substances from the human placenta. For instance, HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) promotes the proliferation of hepatic parenchymal cells for recovery of a damaged liver. Our product safety is ensured by the most rigid safety measures among existing scientific standards.
Warning: As LAENNEC Injection is an ethical drug, JBP has never sold it on Internet.
*COMPOSITION
Each 2 mL ampoule of this product contains 112 mg of a water-soluble human placenta hydrolysis by extracting.
Content per 2 mL
| Component | Content | Remarks | |
| Active ingredient | Water-soluble human placenta hydrolysis by extracting | 112 mg | Component derived from human placenta |
| Inactive ingredients | pH adjuster | Sufficient quantity | – |
Pepsin (porcine gastric mucosal extract) and lactose (bovine, milk) are used in the manufacturing process.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
This product is a light yellow-brown or yellow-brown transparent liquid with a distinctive odor. The pH level ranges from 5.5 to 6.5 and the osmotic pressure ratio (to physiological saline) is approximately one.
INDICATION(S)
Improvement of hepatic function in chronic hepatic disease.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
A normal adult dose is a 2 ml subcutaneous or intramuscular injection once daily. According to symptoms, the dose can be increased to 2 or 3 times daily.
***PRECAUTIONS
1. Careful Administration (LAENNEC should be administered with care in the following patients.)
Patients predisposed to allergies.
2. Important Precautions
[Explanation to patients]
The necessity of this product for disease treatment, as well as the fact that despite the employment of safety measures to prevent the spread of infectious agents at the time of manufacture of this product, the risk of transmission of infectious agents from raw materials derived from human placenta cannot be completely eliminated, should be explained to the patient and every effort made to obtain their understanding.
(1) This product is manufactured from the extract of human placenta delivered full-term in Japan. Each placenta donor has received a medical interview about medical history, travel history, etc.
Furthermore, after screening for viral and bacterial infections by serological examination etc., nucleic acid amplification test (NAT) is performed on HBV-DNA, HCV-RNA and HIV-1-RNA.
In addition, it has been confirmed that high-pressure steam sterilization treatment at 121 °C. for 20 minutes in the production process of this drug has an inactivating effect on various viruses. This product has passed HBV – DNA, HCV -RNA, HIV – 1 – RNA, HTLV – I – DNA, parvovirus B 19 -DNA nucleic acid amplification test (NAT) in product testing. However, there is a possibility that the virus below the limit is contaminated. Since the possibility of infection by this drug administration can not be denied, observe the course after administration adequately.
(2) There have been no reports of transmission of infections, suchas variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), through theadministration of this product in Japan or abroad to date.Nevertheless, it is theoretically impossible to eliminate therisk of transmission of such agents as vCJD completely whenadministering this product, therefore, a enough explanationshould be made to the patient, and the product administeredonly after thorough examination of the necessity of treatment.
(3) Attention must be paid to the indication of this product, which is for the improvement of liver function in chronic liver diseases, and off-label use should be avoided.
3. Adverse Reactions
A total of 10 cases (3.7 %) of adverse reactions or suspected adverse reactions to this product were reported among the 273 patients eligible for safety evaluation in a clinical study performed during implementation of a re-evaluation of drug efficacy (re-examination). The most frequently observed adverse reaction was injection site pain reported in 7 patients (2.6 %), and hypersensitivity (such as rash, fever, and itching), injection site indurations, and gynaecomastia, each in 1 patient (0.4 %). The causal relationship between gynaecomastia and this product is uncertain.
No abnormal changes in laboratory values were observed.1)
(1) Clinically significant adverse reactions
*Shock (incidence unknown):
Since this product contains proteins, amino acids and others derived from human tissue, it may cause shock. The patient should be carefully monitored, and if any signs of abnormalities are observed, administration should be discontinued immediately and appropriate measures taken.
**(2) Other adverse reactions (in descending order of occurrence)
| Injection site pain | 2.56% |
| Hypersensitivity (rash, fever, itching etc.) | 0.37% |
| Injection site indurations | 0.37% |
| Gynaecomastia | 0.37% |
| Impaired liver function (increased AST, ALT etc.) Note | Incidence Unknown |
| Headaches | Incidence Unknown |
Note: Administration should be discontinued if impaired liver function is suspected.
4. Use in the Elderly
Since elderly patients often have reduced physiological function, it should be administrated with care.
5. Pediatric use
The safety of this product in premature infants, newborns, infants, toddlers or children has not been established (No clinical data available).
6. Overdosage
Overdosage of this product and the resulting efficacy or safety has not been established (No clinical data available).
7. Precautions concerning Use
Injection site:
In order to avoid any effect on tissue or nerves, this product should be injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly taking the following precautions:
a) Care should be taken when administering to avoid nerve pathways at the injection site.
b) In the case of repeated injections, avoid injecting into the same site by alternating left and right sides etc.
c) On insertion of the needle, if the patient complains of intense pain or if blood backflow is observed, the needle should be removed immediately, and injected into a different site.
Opening the ampoule:
It is desirable to wipe the part of the ampoule to be cut with an ethanol swab before opening.
PHARMACOKINETICS
The bioactive ingredients of LAENNEC are extracted from human placenta, and the primary pharmacological action of this product cannot be attributed to any single substance or group of substances. Therefore, pharmacokinetic evaluation (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) of this product has not been established.
*CLINICAL STUDIES
Double blind comparative study for chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis1)
Double-blind crossover study evaluating the effect of Laennec in 124 chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis patients in Japan revealed that serum transaminase (GOT, GPT) levels improved significantly by Laennec (see figures below).
Efficacy to GOT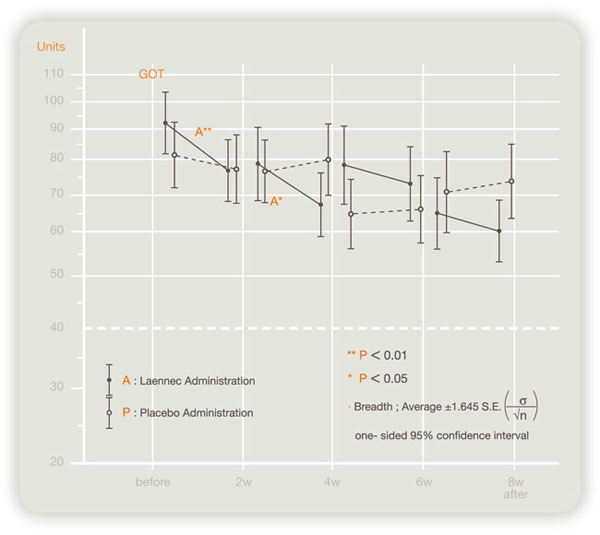
Efficacy to GPT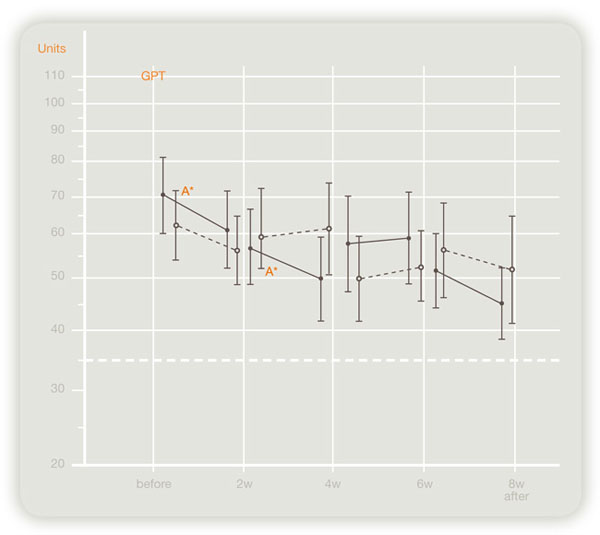
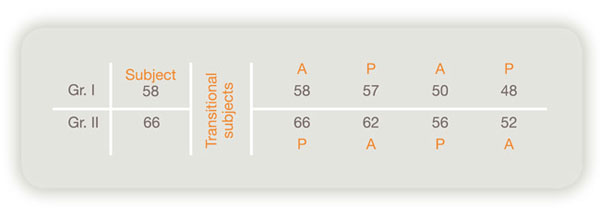
Summary of drug-efficacy
[(A) Items having a tendency to decrease or increase significantly by Laennec]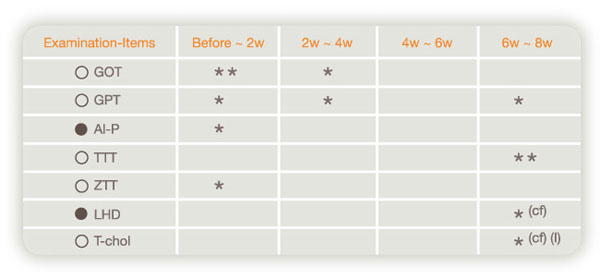
(Data on pharmacological reevaluation)
Summary of drug-efficacy
[(B) Items having a tendency to decrease or increase significantly by Placebo]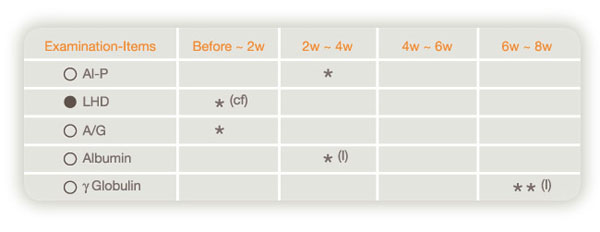

(Data on pharmacological reevaluation)
*PHARMACOLOGY
*1. Promotional effect on liver regeneration2), 3)
Laennec was administered at higher than the clinical dose to healthy rats after 70 % partial hepatectomy and a comparison of liver weight was made over time with control groups. The results revealed a significant promotional effect on liver regeneration in the Laennec groups.
2. Stimulatory effects on cellular DNA synthesis2)
In in vitro study using primary culture rat hepatocytes, a significant DNA-synthesis promoting activity was observed in Laennec group, compared with control groups. In in vivo study, the proportion of hepatocyte nuclei in the DNA synthesis phase in stained liver tissue of ANIT-induced acute hepatitis rat was evaluated. Laennec group, at higher than the clinical dose, showed significant DNA synthesis promotion compared to the control groups.
3. Inhibitory effect on experimental liver injury2), 4)
In in vivo study using ANIT-induced acute hepatitis rat, the serum levels of liver cytosolic enzymes (GPT, ALP, LAP and γ-GTP) and bilirubin significantly decreased in Laennec group at a dose higher than the clinical dose, compared with the control groups.
In addition, in in vivo study using CCl4-induced acute hepatitis and chronic hepatitis rats, Laennec group at a dose higher than the clinical dose, showed a significant decrease in liver cytosolic enzymes in serum (GPT, GOT) and histopathological improvements in liver injury, compared to control groups.
4. Anti-fatty liver effect5)
In vivo study using CCl4-induced acute hepatitis rat, pre-administered Laennec at a dose higher than the clinical dose showed a significant reduction in total liver lipids and total liver cholesterol, compared with the control groups.
5. Inhibitory effect on liver fibroplasia6)
Laennec at a dose higher than the clinical dose exhibited an inhibitory effect on fibroplasia in rat livers which was induced by repeated administrations of CCl4 over 12 weeks. Also, histological finding suggested that even already proliferated interstitial connective tissue had also been absorbed.
PHYSICOCHEMISTRY
This product is a human-placental extract, and contains various biologically active substances.7) However, the active ingredients of this agent cannot be identified as a single substance or group of substances.
*PRECAUTIONS FOR HANDLING
[Record preservation]
As Laennec is designated as a specific biological product, the drug name (brand name), its manufacturing No. or manufacturing code (Lot No.), date of use, the name and address etc. of patients should be recorded upon administration, and the record should be stored for at least 20 years.
Packaging
Boxes of 10 and 50 ampoules
***References
1) Ueda H. et al.: Kanzo, vol.15, 162, 1974
2) Liu K. et al.: Yakuri to Rinsho, vol.5, 2187, 1995
3) Sakamoto K. et al.: Journal of Tokyo Medical University, vol.33, 271, 1975
4) Nakayama S. et al.: Folia Pharmacologica Japonica, vol.94, 137, 1989
5) Sakamoto K. et al.: Journal of Tokyo Medical University, vol.31, 829, 1973
6) Sakamoto K. et al.: Journal of Tokyo Medical University, vol.32, 351, 1974
7) Liu K.X. et al.: J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther. 294(2), 510, 2000
